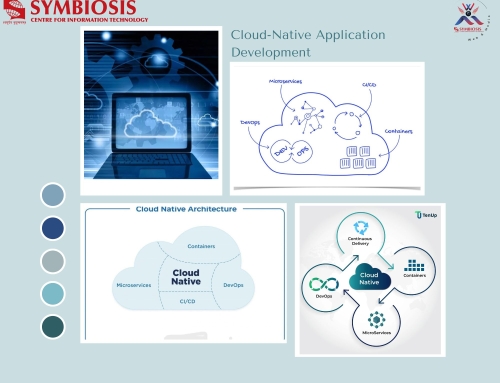
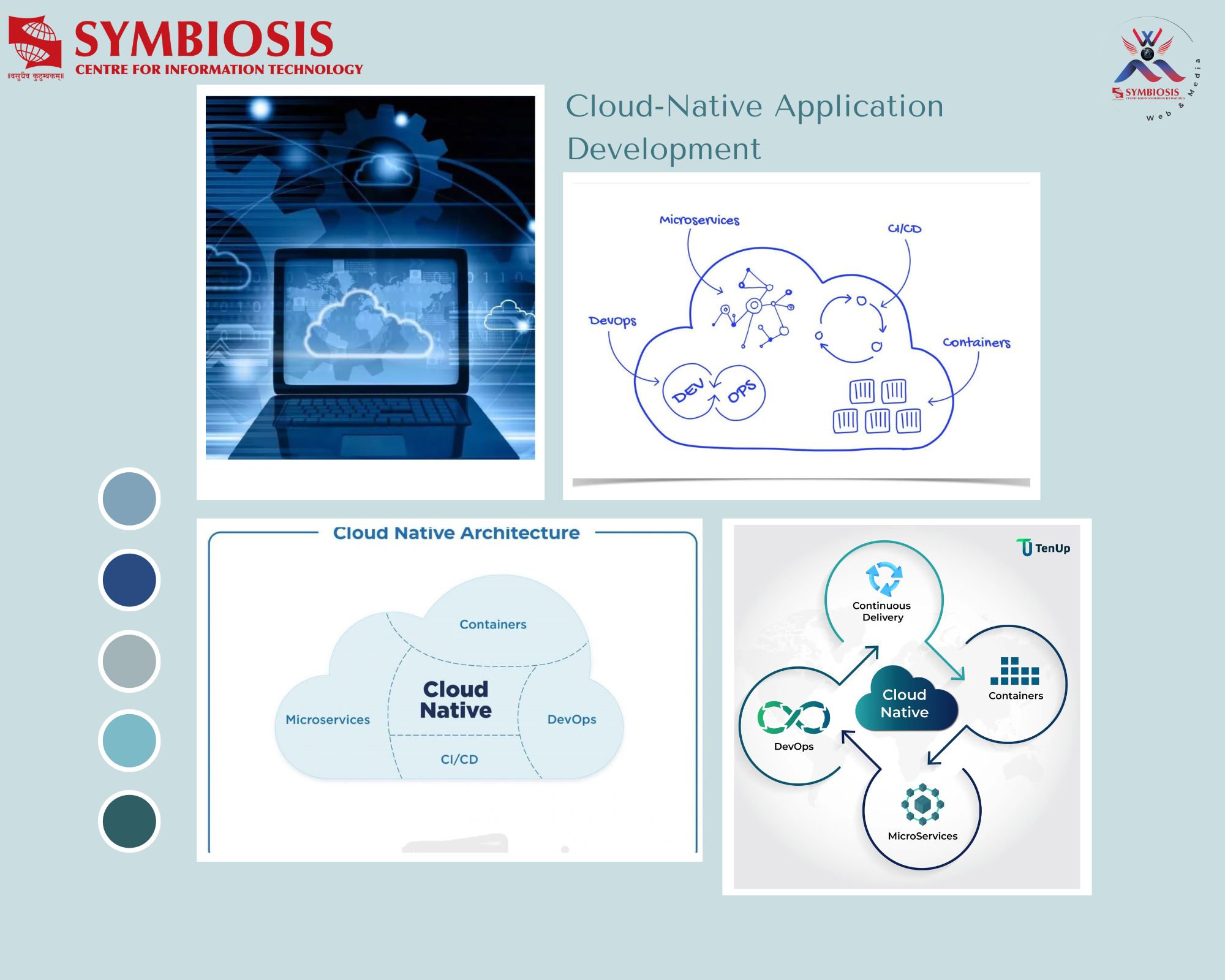
SEXUAL HARASSMENT

Sexual harassment is a violation of women’s human rights and a prohibited form of violence against women in many countries. Sexually harassing conduct causes devastating physical and psychological injuries to a large percentage of women in workplaces around the world. Harassment directed against women in the workplace by their supervisors, fellow employees, or third parties interferes with the integration of women in the workforce, reinforces the subordination of women to men in society, violates women’s dignity and creates a health and safety hazard at work. The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013 is a legislative act in India that seeks to protect women from sexual harassment at their place of work.
Major Features of the Act :-
-The Act defines sexual harassment at the work place and creates a mechanism for redressal of complaints. It also provides safeguards against false or malicious charges.
-The definition of “aggrieved woman”, who will get protection under the Act is extremely wide to cover all women, irrespective of her age or employment status, whether in the organised or unorganised sectors, public or private and covers clients, customers and domestic workers as well.
-While the “workplace” in the Vishaka guidelines is confined to the traditional office set-up where there is a clear employer-employee relationship, the Act goes much further to include organisations, department, office, branch unit etc. in the public and private sector, organized and unorganized, hospitals, nursing homes, educational institutions, sports institutes, stadiums, sports complex and any place visited by the employee during the course of employment including the transportation.
-The Committee is required to complete the inquiry within a time period of 90 days. On completion of the inquiry, the report will be sent to the employer or the District Officer, as the case may be, they are mandated to take action on the report within 60 days.
-Every employer is required to constitute an Internal Complaints Committee at each office or branch with 10 or more employees. The District Officer is required to constitute a Local Complaints Committee at each district, and if required at the block level.
-The Complaints Committees have the powers of civil courts for gathering evidence. -The Complaints Committees are required to provide for conciliation before initiating an inquiry, if requested by the complainant.-Penalties have been prescribed for employers. Non-compliance with the provisions of the Act shall be punishable with a fine of up to INR 50,000. Repeated violations may lead to higher penalties and cancellation of licence or registration to conduct business
Sunil Saroj MBA(ITBM) SCIT- 2013-2015